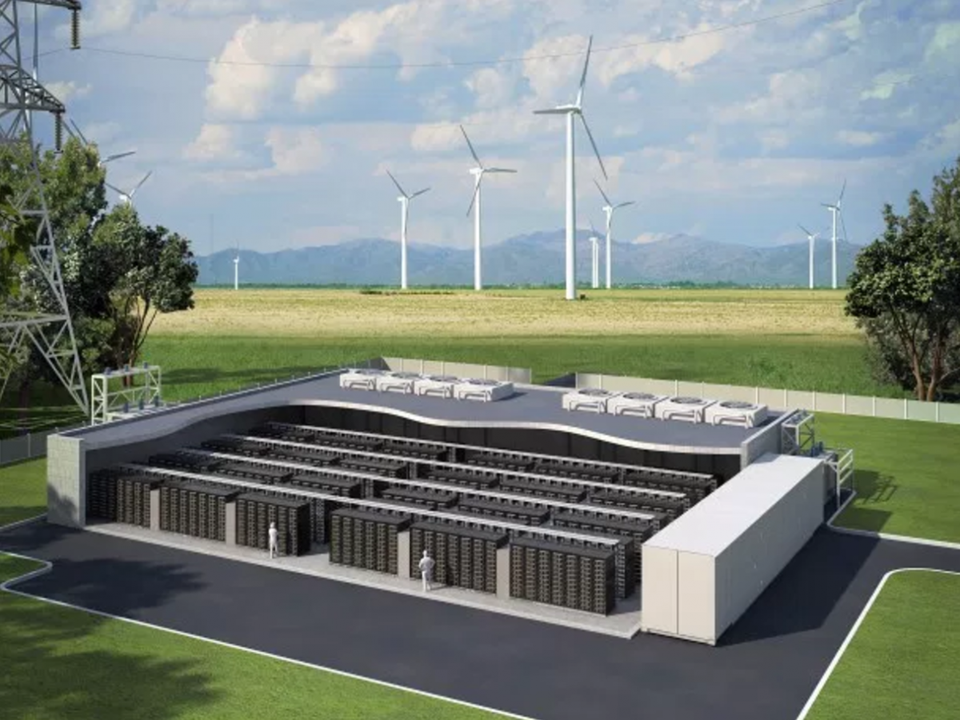
Advanced Industrial Battery Solutions: Powering the Future of Energy Storage
As industries around the globe strive for sustainability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, advanced industrial battery solutions have become an essential tool in the energy sector. These battery solutions offer high-capacity storage, adaptability to various applications, and are integral in managing renewable energy sources. From stabilizing power grids to supporting manufacturing processes, advanced battery solutions empower industries to meet their energy needs while minimizing environmental impact. In this blog, we’ll dive into the importance of advanced industrial batteries, explore the technologies driving them, and discuss their applications across different sectors.
1. The Importance of Advanced Industrial Battery Solutions
In recent years, industries have faced increasing pressure to reduce their carbon footprints and improve energy efficiency. Advanced industrial battery solutions are emerging as powerful assets in addressing these challenges, offering benefits that go beyond conventional energy storage. Here are some key reasons why these solutions are vital:
- Enhanced Energy Storage: Industrial batteries can store large amounts of energy, making them ideal for industries with high energy demands, such as manufacturing, data centers, and telecommunications.
- Integration with Renewable Energy: As renewable energy sources like solar and wind become more prevalent, batteries provide essential storage to harness this intermittent power, balancing supply and demand.
- Cost Savings: By reducing dependency on peak energy from the grid, industrial battery systems allow companies to lower energy costs, especially in regions where energy prices fluctuate throughout the day.
- Grid Stability: Industrial batteries contribute to grid stability by storing energy during low-demand periods and releasing it when demand spikes, which is critical for preventing blackouts and ensuring reliable power.
These advantages are driving rapid adoption of advanced battery solutions across sectors that value efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability.
2. Key Technologies in Advanced Industrial Batteries
The technology behind industrial batteries has seen remarkable advancements in recent years, with innovations that improve performance, longevity, and safety. Some of the most widely used types include:

a) Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are among the most popular choices for industrial applications due to their high energy density, long life, and relatively lightweight construction. Their scalability makes them suitable for applications ranging from small-scale storage to large grid-connected solutions. Additionally, recent developments in lithium-ion technology, like lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, enhance safety and lifespan, making them ideal for industrial use.
b) Solid-State Batteries
Solid-state batteries are an emerging technology that promises higher energy densities and improved safety over conventional lithium-ion batteries. They use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one, which reduces the risk of overheating and enhances durability. Although still in development, solid-state batteries have significant potential for industrial applications, particularly in high-temperature or harsh environments.
c) Flow Batteries
Flow batteries, like vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFB), use liquid electrolytes to store energy, which can be charged and discharged with minimal wear and tear. They are particularly suited for applications that require frequent cycling and long-duration energy storage. Flow batteries excel in grid storage and renewable energy applications, providing a reliable solution for industries that require extended energy support.
d) Sodium-Ion Batteries
Sodium-ion batteries are a newer alternative to lithium-ion, offering lower costs due to the abundance of sodium. While their energy density is lower than lithium-ion, sodium-ion batteries are suitable for large-scale applications where cost is a priority. This technology is particularly promising for industrial applications in energy storage for grids and renewable integration.
3. Applications of Industrial Battery Solutions
The versatility of advanced industrial battery solutions means they can be tailored to meet the energy demands of various industries. Here are some key applications:
a) Manufacturing and Industrial Facilities
Manufacturing plants and industrial facilities typically have high energy demands. Advanced battery systems allow them to store energy during low-demand periods and utilize it during peak hours, reducing energy costs and enhancing operational efficiency. Additionally, battery systems serve as backup power, ensuring production continuity during power outages.
b) Renewable Energy Integration
As more industries shift to renewable energy sources, advanced battery solutions play a critical role in energy storage. For example, solar and wind energy are intermittent sources, meaning they don’t always produce power when it’s needed. Industrial batteries store excess energy generated during peak production times and release it when renewable sources are not available, enabling a smooth and consistent power supply.
c) Data Centers
Data centers require uninterrupted power to protect valuable information and maintain essential digital services. Advanced industrial batteries provide backup power, ensuring that data centers remain operational even during grid failures. Lithium-ion batteries are particularly popular for this application due to their compact size and fast discharge capabilities.
d) Telecommunication Infrastructure
The telecommunications sector requires reliable power to ensure consistent communication networks. Industrial batteries are deployed in telecom towers and facilities to provide backup power, maintain stability, and reduce operational costs. They support telecommunications in remote areas by reducing dependency on diesel generators and minimizing environmental impact.
e) Grid Stabilization
Industrial batteries are crucial in supporting grid infrastructure by managing fluctuations in energy supply and demand. During periods of high energy production, batteries can store excess power and then release it during high-demand periods. This stabilizes the grid, prevents outages, and enables smoother integration of renewable energy into the grid.
4. Benefits of Advanced Industrial Battery Solutions
Advanced industrial battery solutions offer several key benefits that make them essential in modern energy systems:
- Improved Efficiency: These batteries offer high energy density and efficiency, meaning that they can store and release more energy without significant loss.
- Scalability: Industrial battery systems can be scaled to meet the specific needs of different applications, from small commercial setups to large grid-scale solutions.
- Environmental Impact: By reducing reliance on fossil fuels and facilitating renewable energy integration, industrial batteries help industries reduce their carbon footprints.
- Resilience and Reliability: With backup power capabilities, industrial batteries ensure operational continuity even in the event of grid failures, critical for industries that cannot afford downtime.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Industrial batteries enable peak shaving, where stored energy is used during high-cost periods, significantly lowering energy expenses for businesses.
5. The Future of Advanced Industrial Battery Solutions
The future of industrial batteries looks promising, driven by continued innovation and increasing demand for efficient energy solutions. Key trends include:
- Advanced Materials: Research is focused on finding new materials that can enhance battery performance, longevity, and safety, such as silicon anodes in lithium-ion batteries and enhanced electrolytes in solid-state batteries.
- AI and IoT Integration: Artificial intelligence and IoT technologies are being integrated with battery systems to enable smarter energy management. These technologies can optimize charging and discharging cycles, predict maintenance needs, and improve overall efficiency.
- Recycling and Sustainability: As demand for batteries increases, so does the need for recycling. Many companies are investing in processes to recycle lithium, cobalt, and other valuable materials from used batteries, reducing waste and conserving resources.
- Hybrid Systems: Hybrid energy storage systems, which combine different types of batteries or energy sources, are gaining traction. These systems provide flexibility, optimizing performance and cost-effectiveness based on specific energy demands.
- Regulatory Support and Incentives: Governments worldwide are introducing policies and incentives to encourage the adoption of industrial battery solutions, particularly in renewable energy integration and grid stabilization. These policies further boost innovation and make it easier for industries to adopt battery storage solutions.
Conclusion
Advanced industrial battery solutions are reshaping the energy landscape, enabling industries to achieve sustainability goals, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. With technologies like lithium-ion, solid-state, and flow batteries advancing rapidly, the future holds even more possibilities for energy storage solutions that are reliable, scalable, and environmentally friendly. By adopting these solutions, industries can better manage energy demands, support renewable integration, and contribute to a cleaner, greener future. As innovation continues, advanced battery solutions will play a central role in building a sustainable, resilient energy infrastructure.
Get in Touch
Recent Posts
-

CNTE at KEY ENERGY 2026: Showcases STAR H-PLUS Outdoor Liquid-Cooled Energy Storage System
Mar 05, 2026 -

CNTE Honored as 2025 Forbes China Leading Global Brand
Nov 12, 2025 -

CNTE & YOU.ON Partner to Expand Storage Markets
May 19, 2025 -

CNTE Unveils Energy Storage Lineup at Solartech 2025
May 19, 2025 -

CNTE awarded AEO certification
Mar 14, 2025
Tags
- 500 kw battery
- 500 kwh battery price
- all in one solar battery
- at home battery
- battery based energy storage
- battery capacity for solar system
- battery pack for home solar system
- battery pack kwh
- battery power storage systems
- battery storage applications
- battery storage kwh
- battery storage price per kwh
- battery storage suppliers
- battery storage system design
- battery to grid
- bess battery energy
- bess solar system
- better battery renewable energy
- charging station
- clean energy storage solutions
- commercial solar power battery storage
- cost of solar and battery system
- electrical energy storage exhibition
- energy battery pack
- energy storage battery pack
- energy storage system lithium battery
- energy storage system solar
- energy tech battery
- ess battery price
- ess battery system
- ess solar system
- green energy lithium battery
- high capacity battery for solar panels
- hybrid battery storage
- kwh battery storage
- large solar storage batteries
- largest commercial battery
- latest solar batteries
- lithium battery for off grid solar
- lithium battery for solar system price
- lithium battery home storage
- lithium battery packs for solar panels
- new battery storage
- off grid solar battery storage
- on grid battery
- optical storage integration
- outdoor energy storage
- outdoor solar battery cabinet
- pcs battery system
- power pack energy
- price per kwh battery storage
- q cell battery storage
- smart battery storage
- solar and lithium batteries
- solar battery battery
- solar battery container
- solar battery module
- solar battery storage capacity
- solar battery storage container
- solar battery storage manufacturers
- solar cell storage
- solar energy battery storage capacity
- solar energy battery storage system
- solar energy lithium battery
- solar energy storage system price
- solar energy storage technology
- solar ess system
- solar grid battery
- solar installation battery
- solar one batteries
- Solar panel energy storage systems
- solar panel lithium battery storage
- solar panel power storage system
- solar plant battery
- Solar Power Plant Battery
- solar pv and battery storage systems
- solar pv system with battery storage
- solar storage solutions
- solar with battery system
- solar with lithium battery storage
- standalone energy storage systems
- storage energy battery
- storedge battery